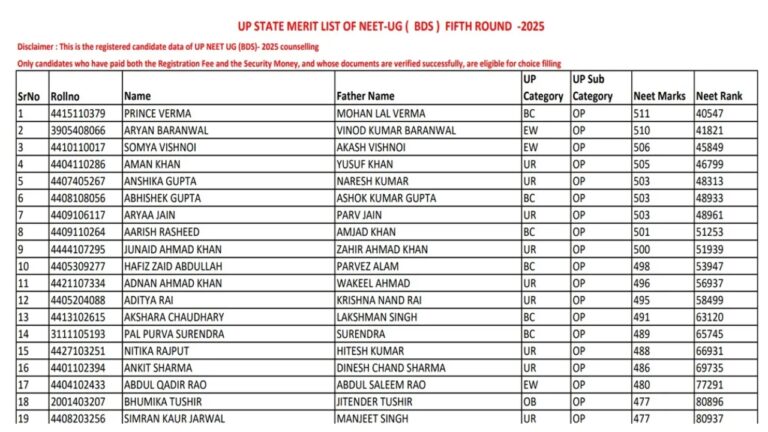
A safe investment means a fixed deposit where your money remains secure. Along with that, you get a guaranteed return at the end of the term. However, fixed deposits are not the only safe investment option. The National Savings Certificate (NSC) is also considered equally safe. In this article, we will share all the details on which option gives higher returns for middle-class investors.
National Savings Certificate vs Fixed Deposit: A Comparison for Safe Investments
A safe investment usually means a fixed deposit, where your money is secure, and you are guaranteed a return at the end of the term. However, there are other safe investment options, such as the National Savings Certificate (NSC), which is considered equally reliable. This article will provide all the details to help middle-class investors decide which option offers higher returns.
1. Lock-in Period & Tenure
The National Savings Certificate (NSC) has a lock-in period of 5 years. On the other hand, fixed deposits can be invested for different periods, ranging from 7 days to 10 years. The interest rates vary for both, with fixed deposits offering rates between 6.5% to 7.5%, while the NSC currently offers a higher interest rate of 7.7%.
2. Government-Backed Security
Both NSC and fixed deposits are safe investment options, but the NSC is a government-backed savings scheme designed for long-term investors who want safe and high returns. NSC offers fixed interest rates and compounded growth on an annual basis, making it ideal for long-term investors.
3. Investment Limits & Tax Benefits
Fixed deposits can be opened at banks or post offices, and the tax-saving facility under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act is only available for five-year fixed deposits. The NSC, part of the Post Office Small Savings Scheme, allows investments starting from Rs. 1000, with no maximum investment limit. You can invest in multiples of Rs. 100 as much as you want.
4. Interest Payment and Compounding
In an NSC, the interest is credited to the investor’s account, with the principal and interest paid out at the time of maturity. Fixed deposits, however, offer the option of receiving interest monthly, quarterly, or at maturity.
5. Renewal Options
The tenure for NSC is 5 years, and the account cannot be renewed after the term ends. In contrast, fixed deposits can be auto-renewed after the tenure ends, allowing the money to be reinvested automatically.
6. Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
When you purchase an NSC, the interest rate is fixed for the entire tenure. Similarly, fixed deposit interest rates are generally fixed at the time of investment. However, fixed deposits offer more flexibility in terms of the investment period, ranging from 7 days to 10 years.
7. Compounding Frequency
The interest in an NSC is compounded annually, while fixed deposits are eligible for quarterly compounding. Both NSC and five-year fixed deposits are eligible for tax savings under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
Which one is best For Middle-Class Investors?
For middle-class investors, NSC offers higher returns (7.7%), annual compounding, and tax benefits under Section 80C with a 5-year lock-in. There’s no maximum investment limit, making it ideal for long-term savings. On the other hand, FD provides flexible tenure (7 days to 10 years), regular interest payouts (monthly/quarterly), and liquidity, but only 5-year FDs qualify for tax benefits. If you want higher returns and tax savings, NSC is better. If you need flexibility and liquidity, FD is the right choice.