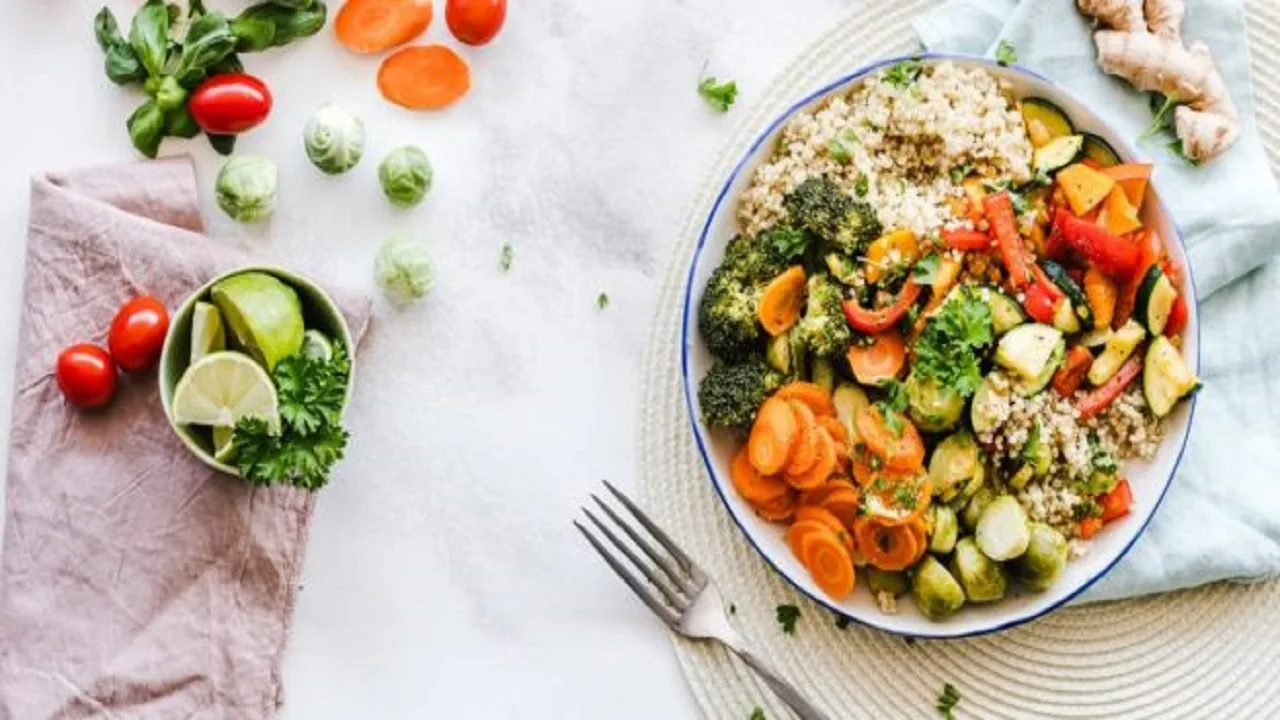
Broccoli, blueberries, walnuts: Certain foods can inhibit inflammation in the body. An anti-inflammatory diet prevents diseases and can alleviate symptoms in those who are ill. But not every food is one of the “good” ones.
How does inflammation occur in the body?
Inflammation is a natural reaction of the immune system that is not bad per se. On the contrary, inflammation is a sign that the body wants to get rid of pathogens or harmful substances – and in the best-case scenario, it succeeds. This process only becomes a problem when the body maintains the inflammatory processes and they continue to smolder undetected. The first signs of this are persistent fatigue, joint pain when getting up, or poor concentration and memory. Over time, hidden inflammation can lead to chronic diseases.
Food that works
Anyone who is concerned about an anti-inflammatory diet should reduce meat, sugar and simple carbohydrates very much. This is because simple carbohydrates such as white flour or sugar cause blood sugar to rise rapidly, which stresses the body and can ultimately lead to inflammation. Another reason to use carbohydrates in moderation: the body’s own fat, especially belly fat, produces hormones that promote inflammation. Anything that increases the waist circumference should therefore be avoided.
And simple carbohydrates are empty calories that hardly fill you up. However, this does not mean completely avoiding carbohydrates. It is just that whole grain products are the better choice. If someone suffers from digestive problems, exhaustion, joint and muscle pain, it may also be sensible to limit the consumption of gluten-containing foodsand replace them with quinoa, amaranth, millet, buckwheat and legumes.
Meat promotes inflammation
Red meat is considered to be inflammatory, which has numerous One reason for this is arachidonic acid. This is an essential omega-6 fatty acid, which, in high concentrations, is responsible for inflammation. Unhealthy saturated fatty acids and trans fats are also found in red meat and sausages.
However, this does not mean that an anti-inflammatory diet has to be purely vegetarian. Meat should only be part of the menu in small quantities and not every day and the quality and preparation of the meat also play a role. Sausages and ready-made products in particular have a high proportion of unhealthy, inflammation-promoting fats and often also a high salt content.
Fat is not the same as fat
If you want to lose weight, you have to avoid fat. That’s a widespread misconception. But not all fat is created equal. Healthy fats are a central component of the anti-inflammatory diet. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, namely the various omega-3 fatty acids, have a strong anti-inflammatory effect. They neutralize the harmful arachidonic acid, which is mostly ingested with meat and cheese.
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in fatty fish such as mackerel, salmon, trout, or herring. The anti-inflammatory diet also includes linseed, chia, and hemp seeds, walnuts, rapeseed oil, wheat germ oil, tofu, and green leafy vegetables. These foods also contain omega-3 fatty acids. Olive oil, olives, and avocados—monounsaturated fatty acids—also help to reduce inflammation.