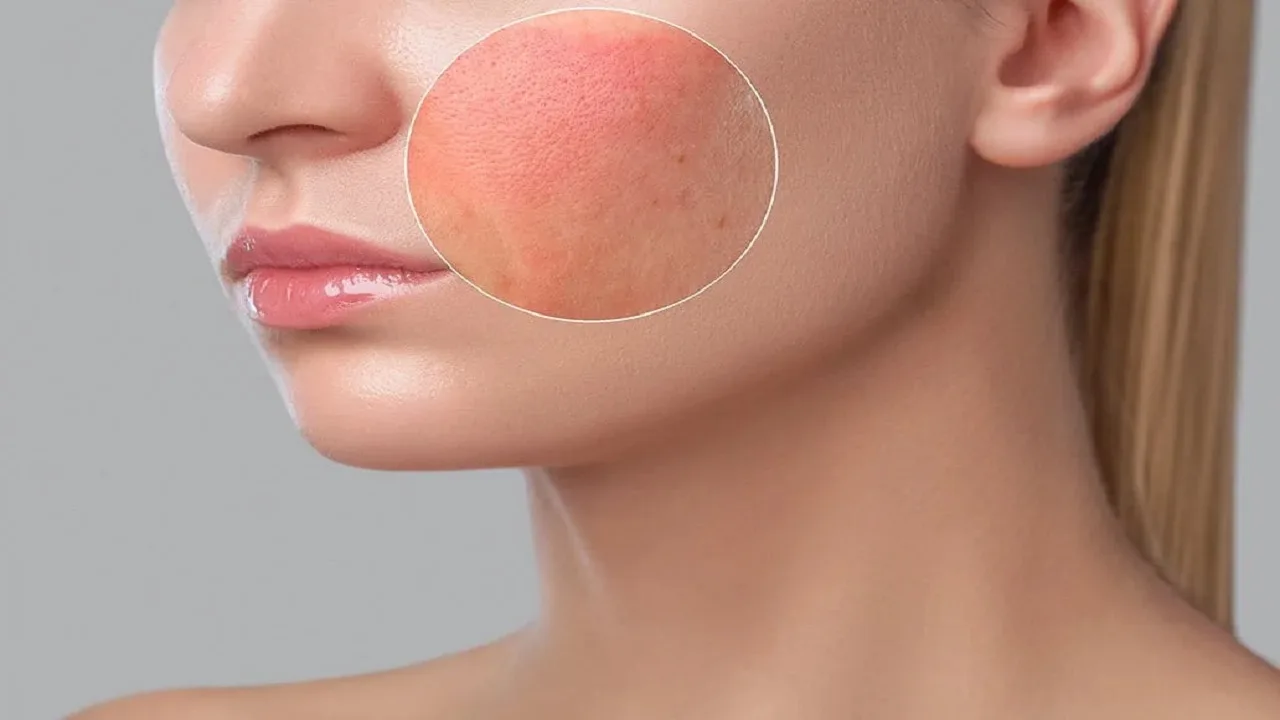
Erythrosis is a pathology caused by the dilation of blood vessels, which usually appears on the face, neck, and hands. The problem compromises the normal functionality of the microcirculation, which, consequently, allows the appearance of localized skin redness. The most common is certainly erythrosis on the face, and if some related diseases are excluded from the diagnosis, the phenomenon is completely benign.
There are, therefore, two types of erythrosis:
- Transient erythrosis, typically of short duration;
- Permanent erythrosis, which may result from chronic disease.
Causes of erythrosis
Skin erythrosis can manifest itself with temporary flashes caused by physiological reasons (fever, effort, anxiety and menopause), be linked to excessive consumption of alcohol, drugs and foods or be the consequence of poor sun exposure. There is also a genetic predisposition and it affects people who have more delicate and fragile capillaries.
Capillary dilation can occur as a consequence of:
- Sunburn that becomes chronic over the years, effectively transforming into erythrosis;
- Erythrosis rosacea ;
- Stage I or II erythrosis rosacea .
All these manifestations are very annoying both from the point of view of the symptoms (the subject who suffers from them, in fact, develops a high sensitivity to atmospheric agents and to the products applied on the affected part) and on a psychological level, causing discomfort in everyday life.
Who is most affected by erythrosis?
When it comes to solar erythrosis, the people most affected are certainly the lighter phototypes and those with sensitive skin . If exposure to the sun does not occur with the necessary precautions, over time the clinical picture of these subjects can worsen until the appearance of permanent chronic erythrosis. The damage caused by UV rays manifests itself over the years, which is why prevention and adequate protection are essential.
How to Prevent Erythrosis on Face and Neck
If the main cause of erythrosis is the sun, it is important to prepare the skin for sun exposure gradually , and protect yourself from UV rays all year round, not just in summer. To prevent erythrosis, it is a good idea to apply a day cream with adequate UV protection even in winter, and it is good practice to cover the neck and décolleté with scarves and natural fabrics throughout the day. In the summer, it is necessary to avoid exposure to the sun’s rays during the central hours of the day and apply protection several times, especially if we are at the beach, in the pool or in the mountains.
It can be helpful to include in our diet foods rich in vitamins that protect the elasticity of the capillaries. We recommend the consumption of:
- Blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, currants and all berries in general because they help strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- Citrus fruits, kiwi, broccoli, peas, cauliflower and green leafy vegetables are rich in vitamins C and K;
Take food supplements that promote microcirculation, such as red vine and bitter orange.
Facial Erythrosis: Treatments and Cure
Treating erythrosis is possible. If we are in the presence of chronic redness, it is necessary to seek the opinion of a dermatologist who will suggest the most appropriate therapy.
Fight erythrosis with specific creams
To treat erythrosis on the décolleté and face, you can help the skin with specific creams and products that reduce redness after just a few uses. For erythrosis, there are various remedies that keep the intense phases and the remission phases at bay. Eucerin, a specialist in dermocosmetics for over 100 years, suggests:
- Eucerin UltraSENSITIVE Cleansing Lotion , which ensures gentle cleansing without irritating or damaging the already suffering and reddened skin barrier;
- Eucerin ANTI-REDNESS Neutralizing Day Treatment with SPF 25 and UVA protection, which provides immediate well-being and relief from redness, to be applied immediately after cleansing, with active ingredients SymSitive and Licochalcone A;
- For immediate relief from redness, try Eucerin ANTI-REDNESS Soothing Night Treatment in the evening , to be used on the face, neck and décolleté to calm unpleasant discomfort and increase the tolerance threshold of hypersensitive skin.