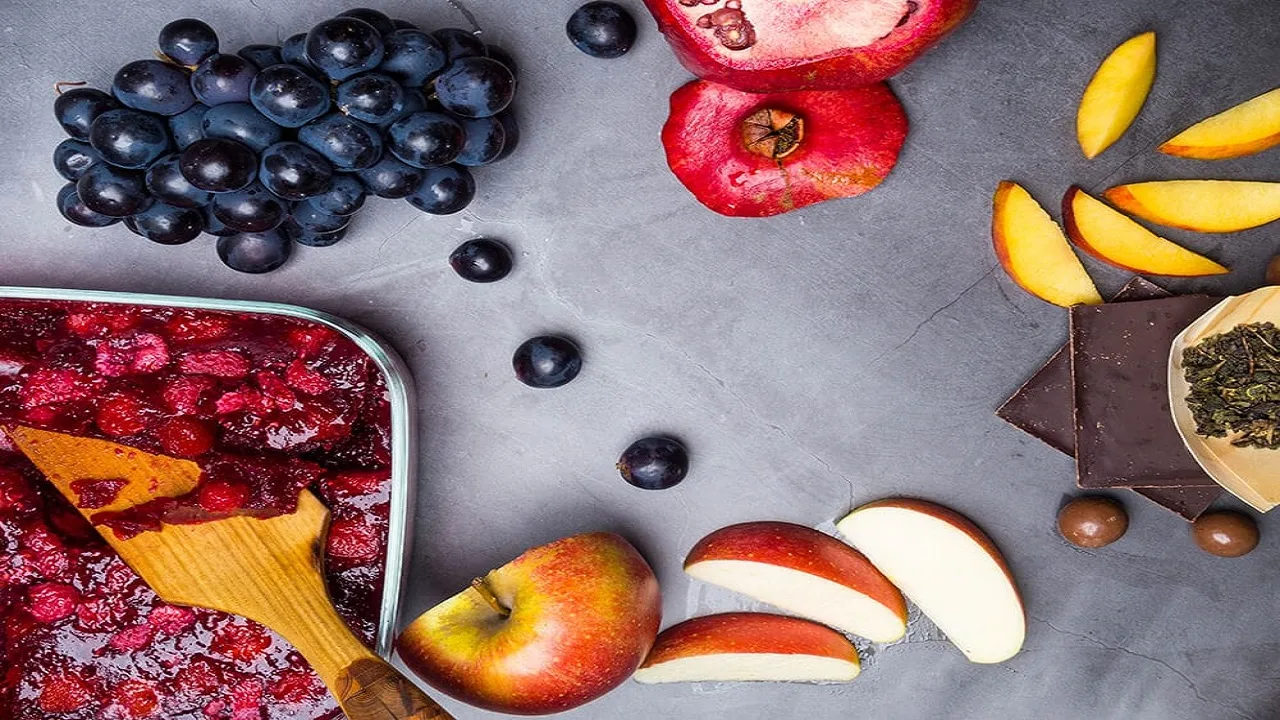
You must have heard the saying, “Color your plate for healthy meals!” The components that give colour to these healthy plates are flavonoids. Flavonoids, which are an important part of daily nutrition, are a group of compounds found in plants and have positive effects on health. They are also pigments that determine the colours, taste and smell of plants. Flavonoids have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They protect the body from the harmful effects of free radicals and can reduce inflammation. Therefore, including colourful plates in your diet and consuming flavonoids regularly is very important for health.
What are flavonoids?
These compounds, which are commonly found in plants, are found in various plant tissues and support the defence mechanisms of plants, helping to protect them from harmful microbes and UV rays. While they benefit many fruits, vegetables and flowers, they also contribute greatly to human health.
The digestion and absorption of flavonoids is different from food groups such as proteins or carbohydrates . They are broken down by intestinal bacteria and used in different parts of the body to benefit from their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They are divided into different subclasses depending on their chemical structure and how they are broken down. Therefore, the benefits of each type of flavonoid are different, and the type of flavonoid you consume will vary depending on the foods you eat.
How many types of flavonoids are there?
Flavonoids, a large family, are divided into many subgroups. The most common subgroups that you can encounter in your daily diet are flavonols, flavones, flavanones, isoflavones and anthocyanidins. Each subgroup mentioned is obtained from different plant sources and has different benefits for health.
- Flavonols: Flavonols are the largest subgroup of the flavonoid family, with over 6,000 types. They are commonly found in many fruits and vegetables, including tea, onions, broccoli, cabbage, lettuce, tomatoes, apples, grapes, and strawberries. They have antioxidant properties and support heart health.
- Flavones: They are commonly found in the leaves and fruit bodies of plants. They protect plants from ultraviolet light (UVB). Food sources that you can consume flavones from include parsley, thyme, celery, hot peppers, and green olives.
- Flavanones : This type of flavonoid is found mostly in citrus fruits like oranges and lemons, as well as grapes. A powerful antioxidant, flavanones cleanse the body of free radicals and support skin health.
- Isoflavones : Found especially in soybeans and other legumes, isoflavones are also known as plant estrogens. They relieve menopause symptoms, support bone health and fight many related diseases.
- Anthocyanins: Pigments found in plants, flowers, and fruits. They are usually found in the outer cell layers of purple, blue, and red fruits such as cranberries, currants, red grapes, merlot grapes, raspberries, strawberries, blueberries, and blackberries. They have antioxidant properties and support brain function.
It reduces the risk of diabetes.
Flavonoids regulate carbohydrate digestion, insulin secretion, glucose uptake and fat accumulation. In this way, they balance insulin and blood sugar. Consumption of fruits such as apples, blueberries and pears, which are rich in flavonoids and have antioxidant properties, helps prevent diabetes. A study has shown that regular consumption of flavonoids and their subclasses reduces the risk of Type 2 diabetes .
Provides a protective effect against cancer.
Studies show that flavonoids have anti-cancer effects and hunt free radicals that can damage large molecules, including DNA. In addition, the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of flavonoids reduce damage and minimize the risk of cancer formation thanks to their protective effects against free radicals and their repairing effects on damaged cells.